Innovation
qXR, deep learning AI software swiftly analyses Chest X-rays to triage scans for patients with lung cancer suspicion, enhancing efficiency and shortening time to diagnosis
Competition
NHS Cancer Programme – Innovation Open Call 1

Clinical Problem
Lung cancer is the biggest cause of cancer deaths in the UK. 5-year survival rate is poor at just 14.6% and 30% of patients die within 90 days of diagnosis, with around 48,600 new cases and 35,300 deaths annually. The National Optimal Lung cancer Pathway (NOLCP) recommends rapid progression from chest X-ray (CXR) to computerised tomography (CT) scan to reduce time to diagnosis for Lung cancer patients. However, radiology capacity and increasing workload hinders implementation of NOLCP, with the current average time at 63 days. Recently published work found that immediate radiographer CXR reporting and triage straight to CT significantly reduced time to diagnosis of Lung cancer by almost half from a median of 32 days compared to routine CXR reporting. Using qXR, an Artificial Intelligence (AI) solution for immediate CXR reporting should have a similar impact on time to diagnosis.
Proposed Solution
qXR is AI-powered X-ray software which will be utilised for triaging CXRs immediately after they have been captured. This triage should allow for quicker and more accurate reporting. The project investigates the impact of AI triage of CXRs against routine non-triaged reporting on time to CT and final diagnosis of a patient. The triage alert could lead to faster reporting of suspicious X-rays reducing the wait time for CT appointments. qXR double-read also enhances accuracy of reporting, potentially improving lung cancer detection. The project tests AI CXR triage using qXR across NHS sites, assessing clinical effectiveness, economic viability, and integration. Data collection measures impact on Lung cancer diagnosis time, influencing NOLCP implementation.
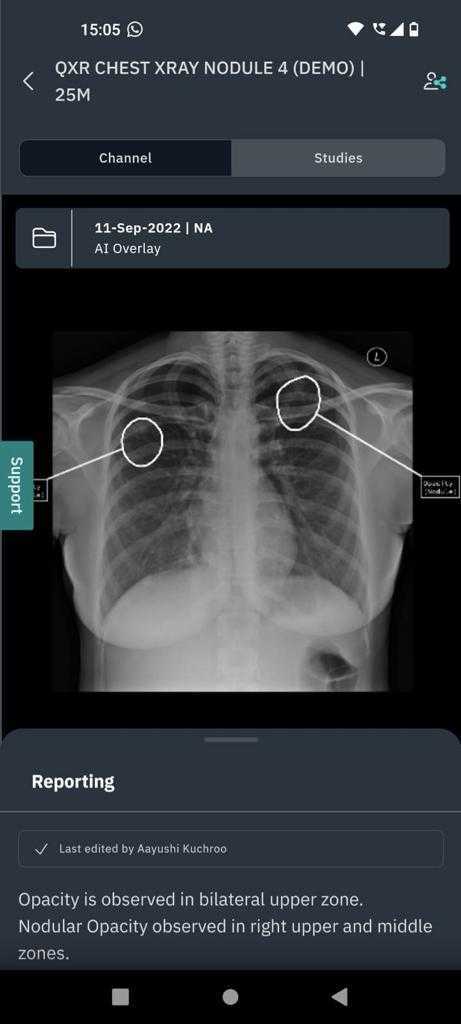
Market Traction and Implementation
• InHealth, the UK’s largest specialist provider of diagnostic and healthcare solutions, has announced a partnership with Qure.ai. Through this partnership, nHealth will be deploying Qure.ai‘s AI solution to aid
in the classification of CXRs into normal and abnormal exams. The solution will be deployed across
InHealth’s entire Tele-reporting service arm to help enhance the quality and accuracy of reporting using
AI.
• India Medtronic Private Limited, a wholly owned subsidiary of Medtronic plc, announced a partnership
with Qure.ai to integrate AI for advanced stroke management in India.
• qXR holds CE Class IIb certification and is clinically validated. It is successfully deployed across LMIC
countries with AstraZeneca and has been tested in the UK for CXR Triage at NHS East Kent, showing
high accuracy and sensitivity.
• Qure.ai announced a new partnership with Therapixel, a French firm that uses AI to improve early breast cancer detection. Qure.ai will be a global distributor for Therapixel’s MammoScreen.
• Medica and Qure.ai have partnered to use Artificial Intelligence to improve the efficiency of workflow and clinical decision support.
• The software is deployed at 1,400 sites globally and is in use in various NHS Trusts, including NHS Frimley Health Foundation Trust, East Kent Hospitals University NHS Foundation Trust, and Greater
Manchester Cancer Alliance. For the current SBRI Healthcare project qXR is deployed at University
College London Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust and University Hospitals of Leicester NHS Trust.
Impact - Early detection and diagnosis of cancer
-
In a recent study conducted with a high sensitivity operating point, qXR had a specificity of 83% on normal versus abnormal triage. The false positive rate would be around 17% (Diagnostics 2022, 12(11), 2724).
-
In a study conducted by Qure.ai with Dubai Health Authority and the University of Sharjah to
evaluate the effectiveness of qXR in detecting lung nodules on CXRs which can be a potential
case of cancer, results showed that qXR had a higher sensitivity of 0.93 as compared to the radiologists’ sensitivity of 0.758. The negative predictive value (NPV) was also high for qXR at 0.956 compared to radiologists (0.87) at 95% confidence interval.
Impact - patient outcomes and experience
Patient feedback supports the need for timely Service delivery reporting. Patients who undergo
investigations are often anxious about the results, with research suggesting that the time between having a test and receiving the results is particularly worrying for the patient. This waiting period is typically characterised by the uncertainty of all possible scenarios. Indeed, reduced anxiety from immediate results was emphasised as a benefit of patients receiving the results at the time of their CXR by the patient panel that supported the initial review of the study design and grant application. "As a patient, the worst thing is the waiting. Once I knew, I felt relieved that there was a diagnosis and that I was doing something about it." [Patient Representative]
Impact - service delivery
Published prospective studies have demonstrated that using AI as an assistance tool can be beneficial
in high-workload healthcare facilities. AI tools with high NPV like qXR can be utilised for screening purposes to screen out normal patients, allowing clinicians to focus more on patients with abnormalities
and their treatment pathways, positively impacting the time spent for screening of abnormal patients.
Clinician quote
"Chest X-rays are frequently performed and for many different reasons. Many chest Xrays are normal; using AI to identify those patients who would benefit most from a rapid report is likely to improve patient outcomes and experience."
Dr Nick Woznitza MBE, Consultant Radiographer & Clinical Academic at University College London Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust & Canterbury Christ Church University
Clinician quote
"Speed of diagnosis is critical to achieve the best outcomes in Lung cancer and to reduce stress and worry for patients. AI solutions such as qXR should improve the pathway logistics by flagging abnormalities on chest X-rays as soon as they are undertaken helping patients to progress rapidly through to CT scanning. This will also assist our incredibly busy workforce."
Professor David Baldwin, Chair, UK Clinical Expert Group for Lung Cancer, NHS England
Date Published
September 2023

